The telephone network has always been made to reduce the number of wires, conveying on a single transmission medium many users as possible.
Analog telephone systems are worked by manipulating the signals using frequency division multiplexing FDM .
With the invention of Pulse Code Modulation (PCM ), ITT took place in Paris in 1939 by Alec Reeves, began the era of digital transmission for telephone signals not telegraph.
Furthermore in the 50th years was perceived the possibility of obtaining a new method of multiplexing, with time division techniques, TDM, instead of frequency.
While in the FDM each user has an exclusive possession of a certain band, in the TDM each user in turn periodically obtains the entire bandwidth for a small time quantum.
PDH
A Holmdel (New Jersey) was born early sixties the U.S. standard of 24 phonic signals converted first into digital PCM techniques and then multiplexed together with the control bits of the weft so as to form a single signal tributary to 1544 Kb / s called DS-1.
A few years later the technology made it possible to put together more DS-1 into a single stream of higher hierarchical level. Since all the switching was analog transmission systems used, each on their own, a quartz clock (to convert analog voice into a digital stream that then riconvertiva arrival in analog) was developed a method called "PDH (Plesiochoronous Digital Hierarchy)".
At the end of the sixties Europeans devised a similar standard, with 30 telephone channels plus a channel for controlling the weft and one for signaling, for a total of 2048 Kb / s. This format is commonly called E1.
When digital transmission began to emerge with a technology acceptable CCITT was unable to reach an agreement on an international standard. The differences are not just about speed, but concern the length of weft and other interesting issues, it would be complex to explain.
The table shows the transmission bit rate at different hierarchical levels in a developed tirthy years until the nineties in various areas of high intensity of telephone traffic.
The European hierarchy is as follows:
- Four E1 2048 Kb / s form an E2 to 8 Mb / s
- Four E2 from 8Mb / s forming an E3 from 34 Mb / s
- Four E3 from 34 form an E4 from 140MB / s
The Telettra realized and installed on a cable Mux E5 (not standardized) from 565 Mb / s format by four E4.
Analog telephone systems are worked by manipulating the signals using frequency division multiplexing FDM .
With the invention of Pulse Code Modulation (PCM ), ITT took place in Paris in 1939 by Alec Reeves, began the era of digital transmission for telephone signals not telegraph.
Furthermore in the 50th years was perceived the possibility of obtaining a new method of multiplexing, with time division techniques, TDM, instead of frequency.
While in the FDM each user has an exclusive possession of a certain band, in the TDM each user in turn periodically obtains the entire bandwidth for a small time quantum.
PDH
A Holmdel (New Jersey) was born early sixties the U.S. standard of 24 phonic signals converted first into digital PCM techniques and then multiplexed together with the control bits of the weft so as to form a single signal tributary to 1544 Kb / s called DS-1.
A few years later the technology made it possible to put together more DS-1 into a single stream of higher hierarchical level. Since all the switching was analog transmission systems used, each on their own, a quartz clock (to convert analog voice into a digital stream that then riconvertiva arrival in analog) was developed a method called "PDH (Plesiochoronous Digital Hierarchy)".
At the end of the sixties Europeans devised a similar standard, with 30 telephone channels plus a channel for controlling the weft and one for signaling, for a total of 2048 Kb / s. This format is commonly called E1.
When digital transmission began to emerge with a technology acceptable CCITT was unable to reach an agreement on an international standard. The differences are not just about speed, but concern the length of weft and other interesting issues, it would be complex to explain.
The table shows the transmission bit rate at different hierarchical levels in a developed tirthy years until the nineties in various areas of high intensity of telephone traffic.
The European hierarchy is as follows:
- Four E1 2048 Kb / s form an E2 to 8 Mb / s
- Four E2 from 8Mb / s forming an E3 from 34 Mb / s
- Four E3 from 34 form an E4 from 140MB / s
The Telettra realized and installed on a cable Mux E5 (not standardized) from 565 Mb / s format by four E4.
The only common agreement at all over the globe was the choice of the sampling frequency, 8Khz, thedouble-2 of the maximum frequency of the speech channel, which was all over the world wide 4KHz.
Each sampled value can not yet be encoded as is susceptible of an infinite number of amplitudes between two extremes predetermined. And 'necessary quantization that divides the interval amplitude in small discrete steps.
In telephony, has adopted 256 discrete levels of quantization. Each level is represented by a code word of 8 bits, accordingly the speed of figure is determined by the ratio between the number of binary digits coding (8) and sampling interval T (125μS) which assumes the value of 64 Kb / S.
The output signal from the encoder (codec) is constituted by a succession of impulses that in code represents the analog signal. For this reason it is called pulse code modulation signal or pulse code modulation.
Instead of having n PCM encoders and merge the result into a single digital signal is sampled the Xn (t) voice signals in a round-robin and the resulting analog stream is passed to the encoder.
The apparatus with which the formation is effected by n signals into a single output stream, is referred to as multiplexer, multiplex or mux simply, the one with which it is realized Li ¿½ operation inversedemultiplexer, demultiplex or demux.
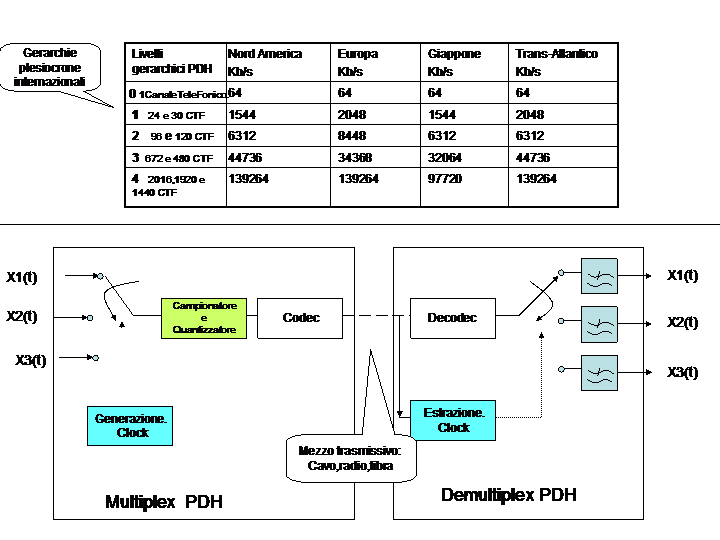
The architecture represented in the figure is used only for the first hierarchical level. After that, to increase the number of channels in a flow need to enter the many cascaded multiplexers.
The amount of information and equipment to be used to locate and extract the single channel is remarkable. The system was the basis of all PDH transmission systems, it is completely flexible, but is the best you could come up in the sixties. He was also the technical reason that justified the telephone monopoly in almost all the nations of the world.
SDH
In the eighties, the U.S. government was convinced that the telephone monopoly was illegal. He denounced the judiciary AT & T and won.
On January 1, 1984, AT & T was divided into 23 companies and other operators entered.
At that time, scientific research led the purity of glass used in optical fiber attenuation values of these to be spread with all the energy, the convenience of the new means of transport.
The new company had to connect with various PDH operators in most systems with different optical TDM.
Was necessary standardization, was built in 1989 and introduced a new method called SONET (Synchoronous Optical Network) which was derived from the 'SDH (Synchoronous Digital Hierarchy),which could:
- Take advantage now that the U.S. was switching systems in numerical and then were synchronized with each other
- Take the opportunity not only to unify American standards, but also those in Europe and Japan, in order to simplify the intercontinental connections.
- Being used for the fiber, for the cable and to the radio.
- Place a minimum of intelligence MUX in order to facilitate operation and maintenance.
- Establish networks with equipment from different manufacturers and different operators.
- Be compatible with existing PDH streams.
This huge standardization work (not yet fully completed) lasted over ten years.
The SDH is much more than an update of the previous standard is a revolution of the telephone network. Beginning was coupled with PDH system and then almost completely replaced. (PDH Today the system has a new life, 2 to a maximum of 34 Mb / s, only for the connection of stations BTS of the mobile radio network).
Was necessary standardization, was built in 1989 and introduced a new method called SONET (Synchoronous Optical Network) which was derived from the 'SDH (Synchoronous Digital Hierarchy),which could:
- Take advantage now that the U.S. was switching systems in numerical and then were synchronized with each other
- Take the opportunity not only to unify American standards, but also those in Europe and Japan, in order to simplify the intercontinental connections.
- Being used for the fiber, for the cable and to the radio.
- Place a minimum of intelligence MUX in order to facilitate operation and maintenance.
- Establish networks with equipment from different manufacturers and different operators.
- Be compatible with existing PDH streams.
This huge standardization work (not yet fully completed) lasted over ten years.
The SDH is much more than an update of the previous standard is a revolution of the telephone network. Beginning was coupled with PDH system and then almost completely replaced. (PDH Today the system has a new life, 2 to a maximum of 34 Mb / s, only for the connection of stations BTS of the mobile radio network).
The fundamental apparatuses, the SDH system, are the ADM (Add Drop Multiplexer) for the insertion and removal of the numerical flows and DXT (Digital Cross Connect) for the permutation of the traffic at the level of aggregate flows.
In the second part of the nineties, in Italy, these systems have been incorporated in large quantities in the backbone fiber from 622 Mb / s to 2.5 Gb / s and radio to 155 Mb / s.
Are present and widespread in the metropolitan area of collection SDH rings that allow you to aggregate traffic in access and channel it towards the junction area.
In the second part of the nineties, in Italy, these systems have been incorporated in large quantities in the backbone fiber from 622 Mb / s to 2.5 Gb / s and radio to 155 Mb / s.
Are present and widespread in the metropolitan area of collection SDH rings that allow you to aggregate traffic in access and channel it towards the junction area.
As to the television signal we have two types of networks. Contribution networks gates opening when the signals from the production centers to the assembly of schedules (playout) and distribution networks carry signals when the playout of broadcast transmission sites to spread to you.
For these networks, RAI still in different areas uses radio frequency modulation for several years and is starting the installation of radio links with SDH 128 QAM modulations.
Instead, the first national network of distribution of digital television signals was made by Mediaset and not use either PDH or SDH systems.
The analog signal converted to digital and compressed to 45 Mb / s used special Coder TV, Modem 64 QAM and 10-GHz radio links, specially designed by Telettra Alcatel Vimercate.
The transmission speed of these modems, is 90 Mb / s and are able to transfer two coded TV signals in high definition.
TV signals the arrival in the transmission sites are decompressed and converted back to analog to be transmitted by the fifth round in UHF band.
Today, in the new systems distribution both analog (PAL) and digital ( DVB MPEG-2 ) using cable, satellite or microwave links PDH 34 Mb / s SDH EA to 155 Mb / s to transfer to four signals TV simultaneously.
For these networks, RAI still in different areas uses radio frequency modulation for several years and is starting the installation of radio links with SDH 128 QAM modulations.
Instead, the first national network of distribution of digital television signals was made by Mediaset and not use either PDH or SDH systems.
The analog signal converted to digital and compressed to 45 Mb / s used special Coder TV, Modem 64 QAM and 10-GHz radio links, specially designed by Telettra Alcatel Vimercate.
The transmission speed of these modems, is 90 Mb / s and are able to transfer two coded TV signals in high definition.
TV signals the arrival in the transmission sites are decompressed and converted back to analog to be transmitted by the fifth round in UHF band.
Today, in the new systems distribution both analog (PAL) and digital ( DVB MPEG-2 ) using cable, satellite or microwave links PDH 34 Mb / s SDH EA to 155 Mb / s to transfer to four signals TV simultaneously.
Notes
1) Plesio, from the greek, meaning "almost". At each speed tributary is allowed an amount of variation, normally of ± 50 ppm (parts per million).
The multiplexer reads every tax at a rate higher clock allowed and, when there are more bits in the buffer (buffer) in entry (because they're coming in a bit slower clock), it adds a bit to "justify" the signal at the highest speed.
The Mux has a mechanism to indicate to the demux the fact that has made a justification, so that this last one knows what is the bit to be deleted.
2) For a sampling frequency lower than twice, the information would be lost at a sampling rate higher than twice, no extra information would be added (on the Shannon sampling theorem)
3) For a variety of reasons, both technical and practical, the shutdown of analog TV can not happen before 2010-2014.